Introduction
Android Componets
UserInterface
Advanced UI
Data Storage
Advanced Concepts
Others
New Studio
Android Bluetooth Tutorial
Bluetooth is a way to exchange data with other devices wirelessly. Android provides Bluetooth API to perform several tasks such as:- scan bluetooth devices
- connect and transfer data from and to other devices
- manage multiple connections etc.
Android Bluetooth API
The android.bluetooth package provides a lot of interfaces classes to work with bluetooth such as:- BluetoothAdapter
- BluetoothDevice
- BluetoothSocket
- BluetoothServerSocket
- BluetoothClass
- BluetoothProfile
- BluetoothProfile.ServiceListener
- BluetoothHeadset
- BluetoothA2dp
- BluetoothHealth
- BluetoothHealthCallback
- BluetoothHealthAppConfiguration
BluetoothAdapter class
By the help of BluetoothAdapter class, we can perform fundamental tasks such as initiate device discovery, query a list of paired (bonded) devices, create a BluetoothServerSocket instance to listen for connection requests etc.Constants of BluetoothAdapter class
BluetoothAdapter class provides many constants. Some of them are as follows:- String ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE
- String ACTION_REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE
- String ACTION_DISCOVERY_STARTED
- String ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED
Methods of BluetoothAdapter class
Commonly used methods of BluetoothAdapter class are as follows:- static synchronized BluetoothAdapter getDefaultAdapter() returns the instance of BluetoothAdapter.
- boolean enable() enables the bluetooth adapter if it is disabled.
- boolean isEnabled() returns true if the bluetooth adapter is enabled.
- boolean disable() disables the bluetooth adapter if it is enabled.
- String getName() returns the name of the bluetooth adapter.
- boolean setName(String name) changes the bluetooth name.
- int getState() returns the current state of the local bluetooth adapter.
- Set
getBondedDevices() returns a set of paired (bonded) BluetoothDevice objects. - boolean startDiscovery() starts the discovery process.
Android Bluetooth Example: enable, disable and make discovrable bluetooth programmatically
File:activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView android:text=""
android:id="@+id/out"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</TextView>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="49dp"
android:text="TURN_ON" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button1"
android:layout_below="@+id/button1"
android:layout_marginTop="27dp"
android:text="DISCOVERABLE" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button2"
android:layout_below="@+id/button2"
android:layout_marginTop="28dp"
android:text="TURN_OFF" />
</RelativeLayout>
Provide Permission
You need to provide following permissions in AndroidManifest.xml file.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
File: AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.bluetooth"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="16" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.bluetooth.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Let's write the code to enable, disable and make bluetooth discoverable.File:
MainActivity.java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private static final int REQUEST_ENABLE_BT = 0;
private static final int REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE_BT = 0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final TextView out=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.out);
final Button button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
final Button button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
final Button button3 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button3);
final BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null) {
out.append("device not supported");
}
button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
if (!mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);
}
}
});
button2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
if (!mBluetoothAdapter.isDiscovering()) {
//out.append("MAKING YOUR DEVICE DISCOVERABLE");
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "MAKING YOUR DEVICE DISCOVERABLE",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_DISCOVERABLE_BT);
}
}
});
button3.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
mBluetoothAdapter.disable();
//out.append("TURN_OFF BLUETOOTH");
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "TURNING_OFF BLUETOOTH", Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
Android Wifi Example
The android.net.wifi.WifiManager class can be used to manage the wifi connectivity. It can be used to add network, disable network, scan for access points, disconnect etc.Android wifi example to enable and disable wifi
Let's see the simple example of wifi to enable and disable the wifi service.File:
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="76dp"
android:layout_marginTop="67dp"
android:text="Enable Wifi" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button1"
android:layout_below="@+id/button1"
android:layout_marginTop="44dp"
android:text="Disable Wifi" />
</RelativeLayout>
File: MainActivity.java
import android.net.wifi.WifiManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button enableButton,disableButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
enableButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
disableButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
enableButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
WifiManager wifi = (WifiManager) getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
wifi.setWifiEnabled(true);
}
});
disableButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v){
WifiManager wifi = (WifiManager) getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
wifi.setWifiEnabled(false);
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
Add Permission in AndroidManifest.xml
You need to add following permissions in AndroidManifest.xml file.File:
AndroidManifest.xml
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE"/>
OUTPUT :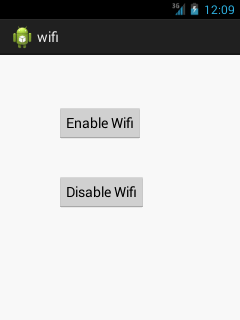
Android Sensor Tutorial
- Sensors can be used to monitor the three-dimensional device movement or change in the environment of the device.
- Android provides sensor api to work with different types of sensors.
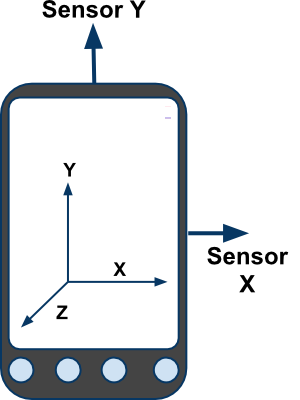
Types of Sensors
Android supports three types of sensors:- Motion Sensors :
These are used to measure acceleration forces and rotational forces along with three axes. - Position Sensors :
These are used to measure the physical position of device. - Environmental Sensors :
These are used to measure the environmental changes such as temperature, humidity etc.
Android Sensor API
Android sensor api provides many classes and interface. The important classes and interfaces of sensor api are as follows:1) SensorManager class
The android.hardware.SensorManager class provides methods :- to get sensor instance,
- to access and list sensors,
- to register and unregister sensor listeners etc.
SensorManager sm = (SensorManager)getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
2) Sensor class
The android.hardware.Sensor class provides methods to get information of the sensor such as sensor name, sensor type, sensor resolution, sensor type etc.3) SensorEvent class
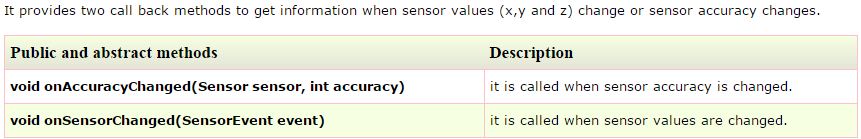
Its instance is created by the system. It provides information about the sensor.4) SensorEventListener interface
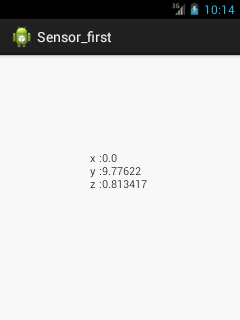
Android simple sensor app example
Let's see the two sensor examples.- A sensor example that prints x, y and z axis values. Here, we are going to see that.
- A sensor example that changes the background color when device is shuffled.
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:androclass="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="92dp"
android:layout_marginTop="114dp"
android:text="TextView" />
</RelativeLayout>
Let's write the code that prints values of x axis, y axis and z axis.File:
MainActivity.java
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
SensorManager sm = null;
TextView textView1 = null;
List list;
SensorEventListener sel = new SensorEventListener(){
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) {}
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
float[] values = event.values;
textView1.setText("x: "+values[0]+"\ny: "+values[1]+"\nz: "+values[2]);
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
/* Get a SensorManager instance */
sm = (SensorManager)getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
textView1 = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
list = sm.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);
if(list.size()>0){
sm.registerListener(sel, (Sensor) list.get(0), SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
}else{
Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), "Error: No Accelerometer.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
if(list.size()>0){
sm.unregisterListener(sel);
}
super.onStop();
}
}
OUTPUT :